PROMPT Therapy
PROMPT is an acronym for Prompts for Restructuring Oral Motor Phonetic Targets. The PROMPT system is described as one which utilizes tactile cues of pressure, place, and timing to promote and enhance effective neuro-muscular innervation and coordination for the learning and integration of motor-speech behaviours (Chumpelik, (Hayden), D. A., The Prompt System: Theoretical Framework and Applications for Developmental Apraxia of Speech, 1981.)
PROMPT creates a unique program for each person based on a combination of many factors to support speech production changes. PROMPT looks at each individual to determine how to develop the most normalized and flexible motor control, cognitive skills and social interactions in the quickest way with the most functional results. PROMPT was developed with children who have a severe motor impairment in mind. PROMPT is a dynamic system theoretical position utilizes tactual sensory information (in addition to auditory and visual) support and develop speech-motor function leading to improved communication function across all domains.
All other forms of therapy for children with motor speech impairments, such as apraxia, focus on the visual and auditory domains. These domains are not adequate to progress children with apraxia. Children with apraxia have a gap of 2 standard deviations between their receptive language (or what they understand and comprehend) and their expressive language (what they are able to verbalize/vocalize). The formal definition of apraxia, as taken from the Terminology of Communication Disorders: Speech-Language-Hearing; Fourth Edition, states that apraxia is a disruption in the ability to transmit or express a motor response along a specific modality; involves disruption of voluntary or purposeful programming muscular movements while involuntary movements remain intact; characterized by difficulty in articulation of speech, formation of letters in writing, or in movements of gesture and pantomime. 2. In speech, a monolinguistic sensorimotor disorder of articulation characterized by impaired capacity to program musculature and the sequencing of muscle movements (respiratory, laryngeal, and oral) for the volitional production of phonemes.
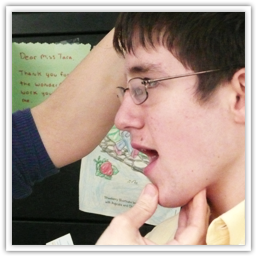
PROMPT is the only technique that targets the sensorimotor and programming difficulties of this disorder. PROMPT is a ‘hands-on’ approach where by the information is not only delivered to the child through auditory and visual modalities, but through tactile-kinesthetic modalities. PROMPT shapes the individuals articulators into the appropriate place for each sounds of each word. According to Chumpelik (Hayden) (1984) the PROMPT system imposes control on the articulators by providing tactile and kinesthetic (closed-loop) feedback, while guiding the structures toward sequential, feed-forward (open-loop) programming. The general effect is one of reducing inadequate feedback and providing correct movement sequences in order to help establish “normal” speech-motor production.
To become a PROMPT Certified Therapist is quite a tedious and stringent process. First, one must enroll in a 3-day long workshop and then return to their place of practice and utilize the technique for 4 months. After the end of four months the ‘trainee’ must then complete a project of self critiques and video tapes and return this information to his/her instructors. The instructors will then review the information form that individual and decide what step they are ready for next. Options include resubmitting the project, retaking the introduction course, or enrolling in the next course Bridging PROMPT: Technique to Intervention. They may enroll in the final course only after practicing for a full 6-12 months after the completion of the initial course. After taking the 3 day Bridging course, after which trainees may refer to themselves as advanced PROMPT trained, they must then practice for at least one full year before applying to take the certification exam. To complete the examination the trainee is required to complete a four month longitudinal project of analysis, program development and implementation, and critique of performance. This again is sent to the PROMPT Institute for review. They will then determine if the trainee passes or requires additional training. So, as you can see, it is a very structured, rigorous, and monitored program that not everyone is qualified to perform after attending one course. It is a new way to assess and deliver services to the motor disordered population where the results are astounding.




 Evaluations
Evaluations